Migrate Your SQL Azure Data to MariaDB – Effortlessly!
This clear guide demonstrates how to transfer your data from SQL Azure to MariaDB efficiently using ESF Database Migration Toolkit.- Execute a step-by-step, reliable migration process.
- Simplify complex data transfers with an intuitive tool.
- Save significant time and effort with automation.
- Modernize your data infrastructure with ease.
Prerequisite:
Software Required:
ESF Database Migration Toolkit »System Supported:
- Windows 7 or higher.
- SQL Azure.
- MariaDB 5.1 or higher.
Step by Step Wizard:
-
Configure SQL Azure Connection
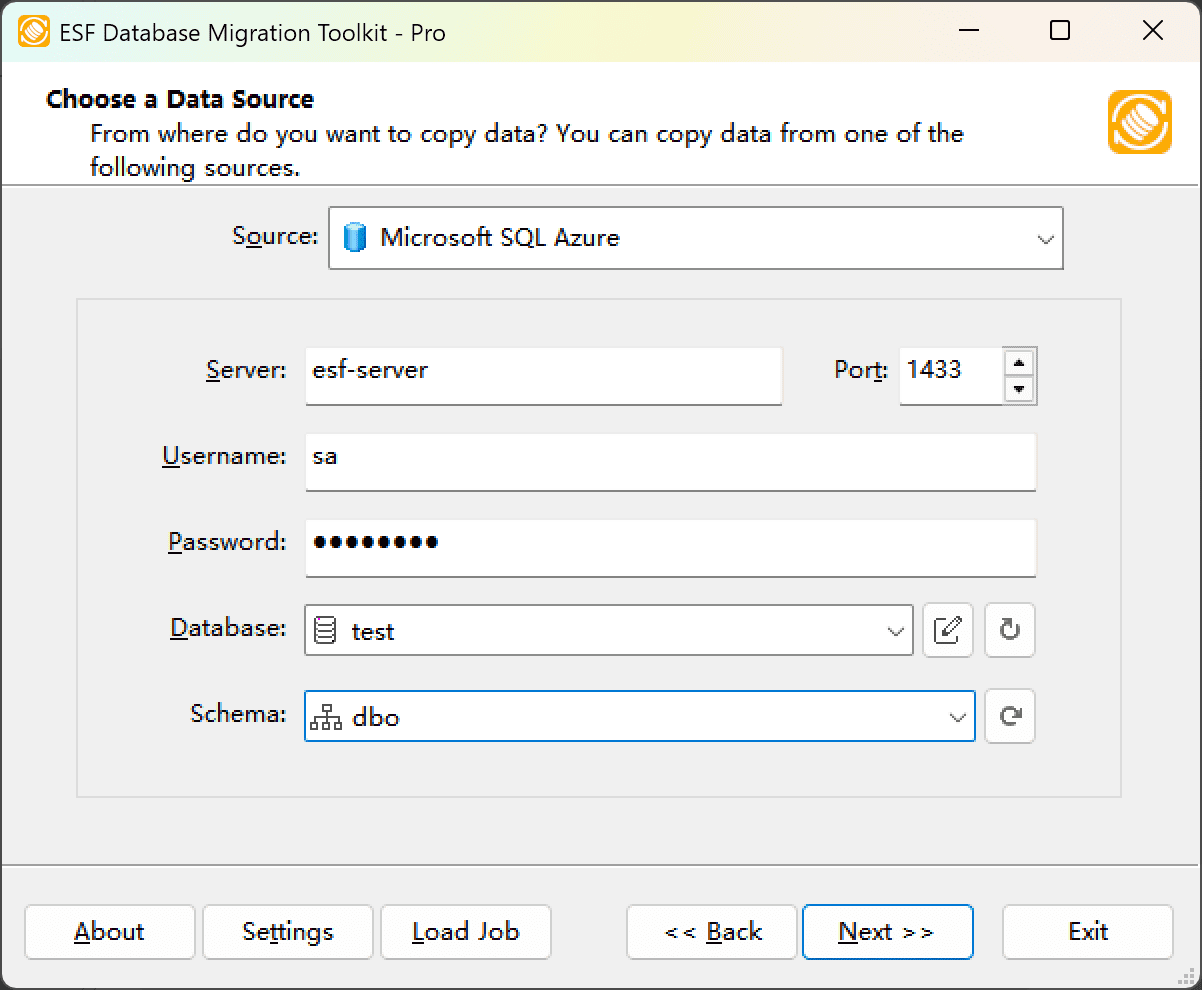
Fig. 1: SQL Azure data source configuration - Prerequisite:
- Enable "Allow access to Azure services" in Azure SQL server settings
- Add your client IP under Firewalls and virtual networks
- In the "Choose a Data Source" dialog:
- Select "SQL Azure"
- Enter connection details:
- Server name: e.g.,
esf.database.windows.net - Port:
1433(default) - Authentication: Enter credentials
- Server name: e.g.,
- Load database options:
- Click the Refresh Database button
- Select target database from list
- Load schema options:
- Click the Refresh Schema button
- Choose desired schema
- Prerequisite:
-
Configure MariaDB Destination
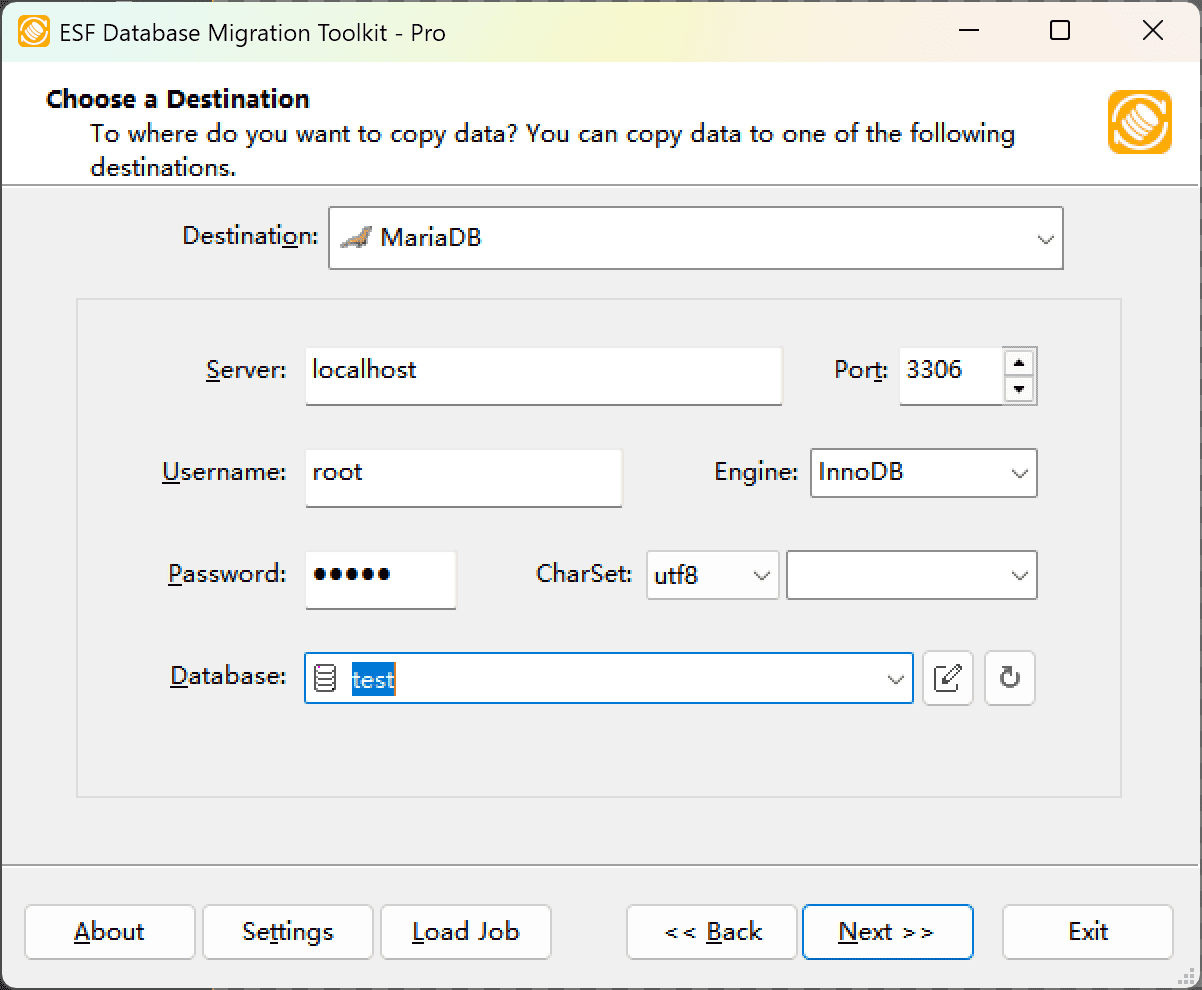
Fig. 2: MariaDB destination configuration - In the "Choose a Destination" dialog:
- Select "MariaDB"
- Enter connection details:
- Server name:
localhost(default) - Port:
3306(default) - Username
- Password
- Server name:
- Optional settings:
- Select MariaDB Storage Engine
-
Choose character set (e.g.,
UTF-8)
- Database configuration:
- Click the Refresh button to list available databases
- Select existing database OR enter new database name
- Note: Non-existent databases will be automatically created during migration
- In the "Choose a Destination" dialog:
-
In "Select Source Table(s) & View(s)" Dialog
-
Select migration objects: Choose tables or views to include in the migration.
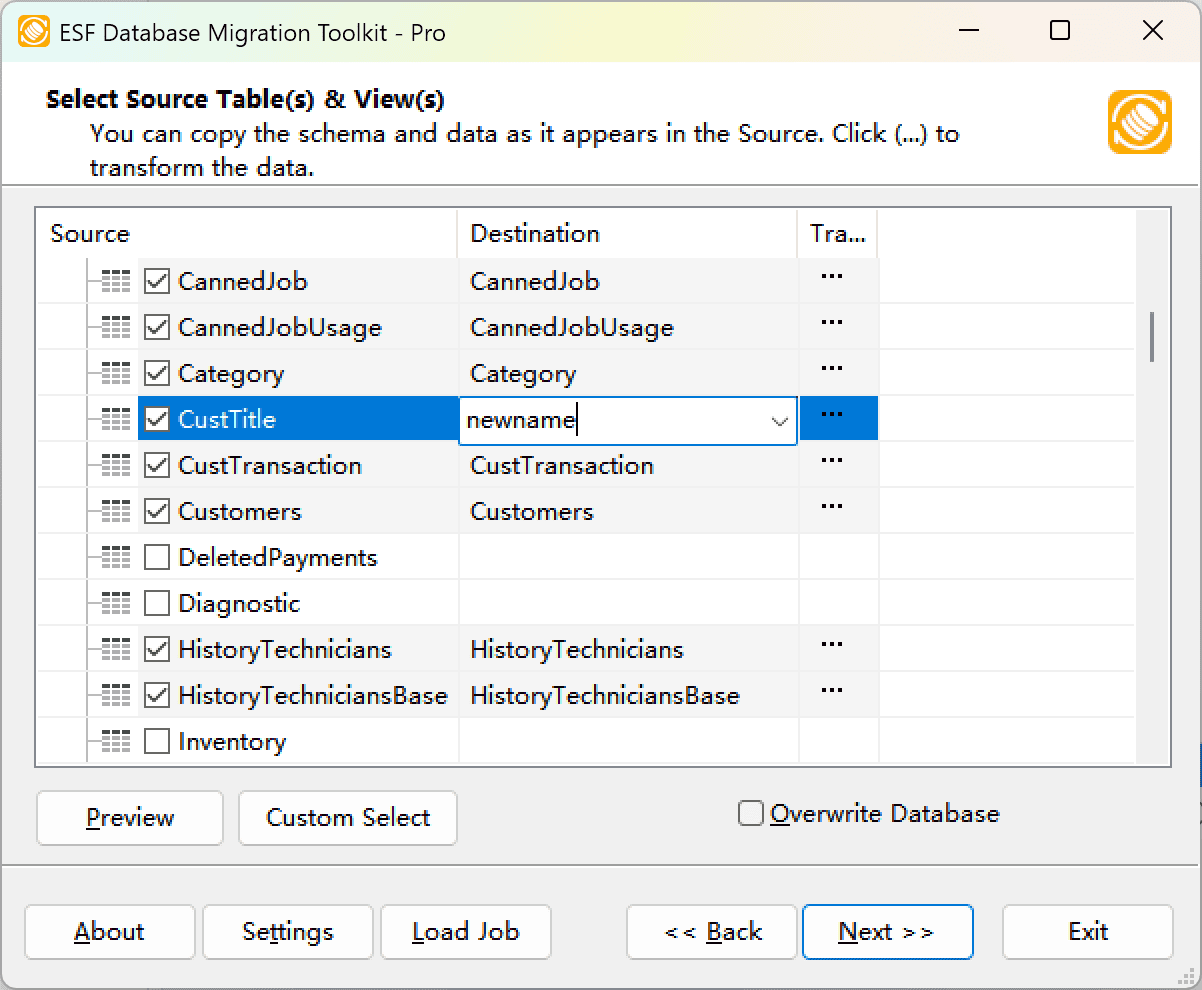
Fig. 3: Select tables and views -
Modify table structure: Click the ellipsis (...) button to access table options and schema adjustments.
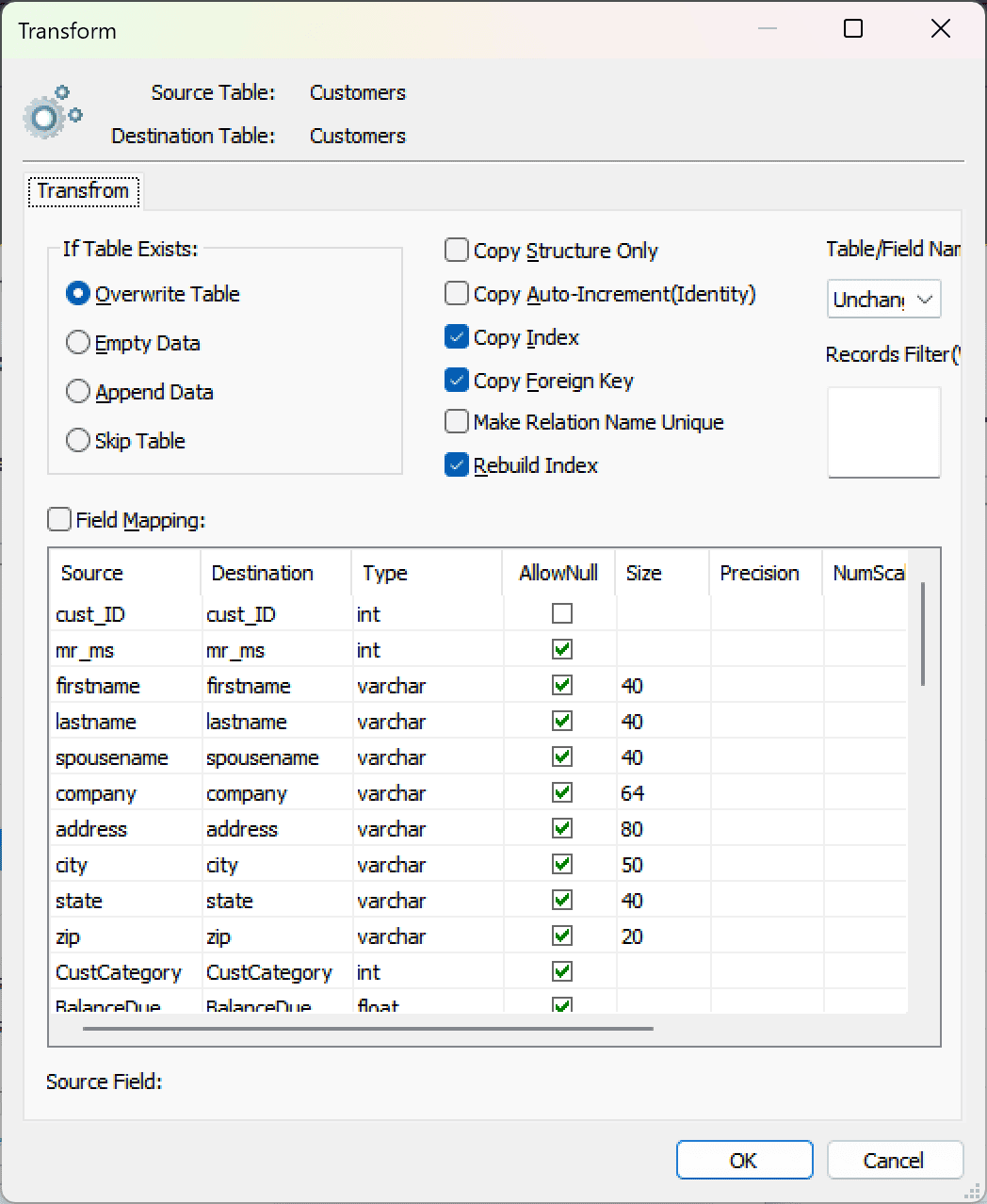
Fig. 4: Do transform -
Configure field mapping: In the Field Mapping options:
- Customize destination fields (name, data type, default value, comments)
- Select data transfer method:
- Overwrite Table (replace existing data)
- Empty Data (truncate before insert)
- Append Data (add to existing data)
- Skip Table (exclude from transfer)
- Apply data filters before transfer
-
Select migration objects: Choose tables or views to include in the migration.
-
Execution Dialog
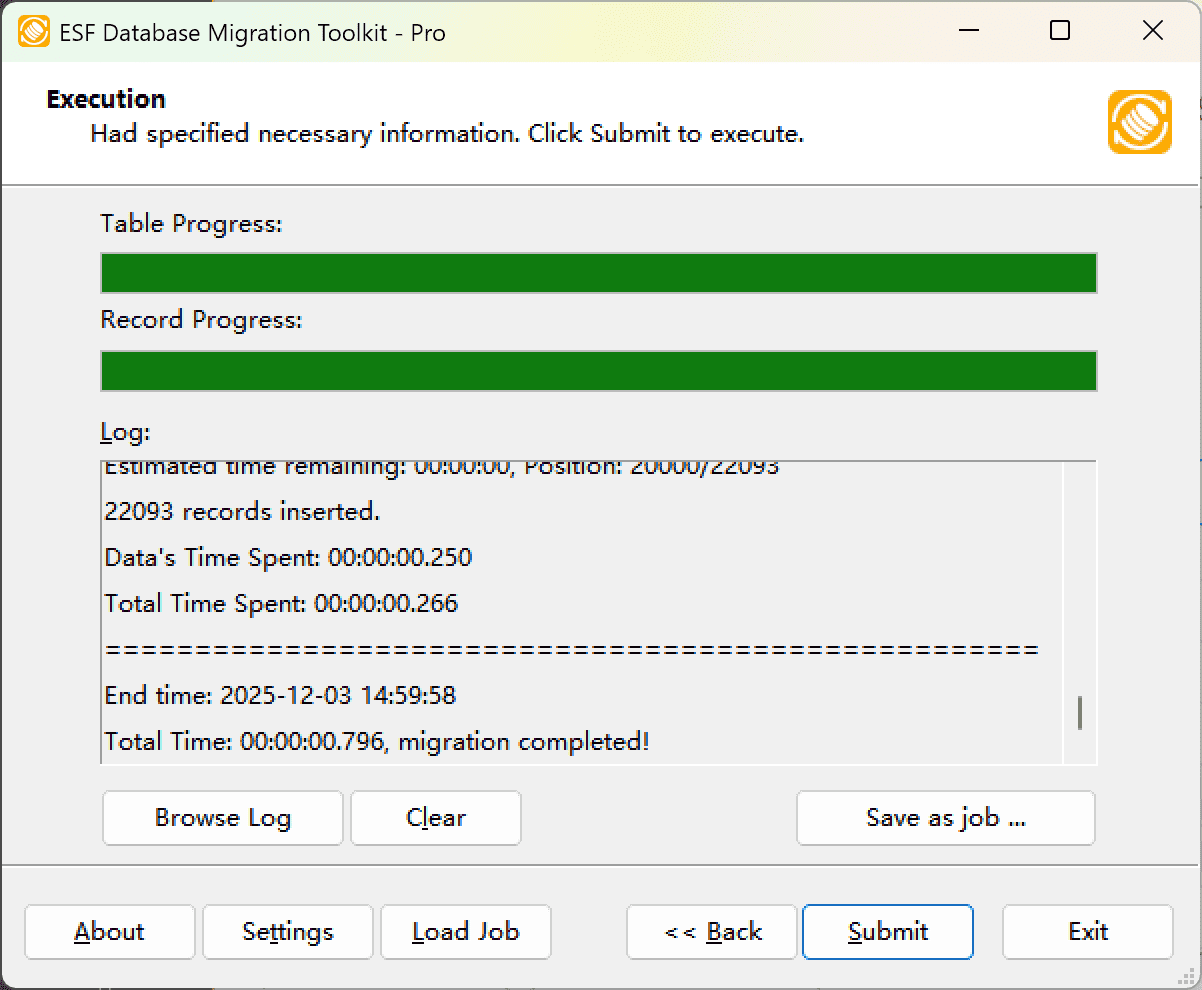
Fig. 5: Execute migration - Start migration: Click "Submit" to initiate automated data transfer from SQL Azure to MariaDB.
- Monitor progress: Click "Browse Log" for real-time migration tracking, including issue resolution details.
-
Save configuration: Click "Save as job" to store settings for:
- Quick reloads of migration jobs
- Command-line execution (use:
dmtc.exe --helpfor parameter options)
-
Migration Completed
Congratulations! Your data migration from SQL Azure to MariaDB has finished successfully. This toolkit generates a comprehensive report for verifying migration accuracy. You can monitor progress as the automated process runs efficiently. For any questions or feedback, contact us – our team is ready to assist.